Mastering Image Formats: Tips and Tools for Graphic Design and Photography
When it comes to images and graphics, understanding the different file formats and their uses is crucial. Each format serves a specific purpose, and choosing the right one can significantly impact the quality and functionality of your work. This guide will help you navigate the world of image formats, including PNG, and offer tips for optimizing images for various purposes.
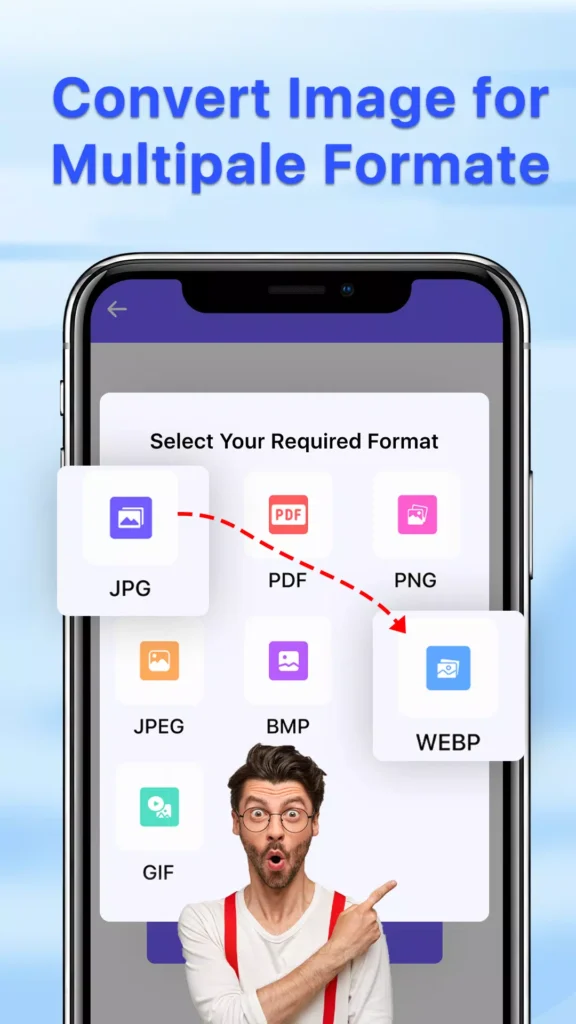
Understanding Image Formats
1. JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group):
- Uses: Best for photographs and images with gradients.
- Pros: High compression, small file size, widely supported.
- Cons: Lossy compression, which means some quality is lost each time the image is saved.
2. PNG (Portable Network Graphics):
- Uses: Ideal for graphics, logos, and images with transparent backgrounds.
- Pros: Lossless compression, supports transparency, high quality.
- Cons: Larger file size compared to JPEG.
3. GIF (Graphics Interchange Format):
- Uses: Best for simple graphics and animations.
- Pros: Supports animation, small file size.
- Cons: Limited to 256 colors, not suitable for detailed images.
4. BMP (Bitmap):
- Uses: Used in Windows systems for simple images.
- Pros: No compression, high quality.
- Cons: Large file size, not suitable for web use.
5. TIFF (Tagged Image File Format):
- Uses: Preferred for printing and publishing.
- Pros: Lossless compression, high quality, flexible format.
- Cons: Large file size, less common for web use.
Tips for Choosing the Right Image Format
1. Consider the Purpose:
- For web use, JPEG and PNG are the most common formats due to their balance of quality and file size.
- For print, TIFF is often preferred because it retains high quality.
2. Think About Compression:
- Use JPEG for photos where file size is a concern.
- Use PNG for images that require transparency and high quality.
3. Optimize for Web Use:
- Compress images to reduce file size without losing quality. Tools like TinyPNG or JPEG Optimizer can help.
Exploring Image Conversion Tools
There are many tools available for converting images between different formats. Here’s a look at a few popular ones:
1. GIMP (GNU Image Manipulation Program):
- Features: Comprehensive image editing suite, supports multiple formats.
- Pros: Free, open-source, highly versatile.
- Cons: Steeper learning curve.
2. Adobe Photoshop:
- Features: Industry-standard editing tools, extensive format support.
- Pros: Powerful, professional-grade features.
- Cons: Subscription-based, expensive for occasional users.
3. Convertio:
- Features: Online file conversion tool, supports a wide range of formats.
- Pros: Easy to use, no software installation required.
- Cons: Internet connection required, may have file size limitations.
Addressing Common Image Editing Questions
1. Why Should I Use PNG for Graphics?
- PNG is ideal for graphics because it supports transparent backgrounds and provides high-quality, lossless compression. This makes it perfect for logos, icons, and detailed images used in design projects.
2. How Can I Convert Multiple Images at Once?
- Many image conversion tools, including batch processing features in Photoshop and GIMP, allow you to convert multiple images at once. This can save time and ensure consistency across your projects.
3. Will Converting Images Affect Quality?
- Using formats like PNG and TIFF, which offer lossless compression, ensures that the image quality is maintained. However, converting images to JPEG may result in some quality loss due to its lossy compression method.
4. Can I Adjust Transparency in My Images?
- Yes, many image editing tools allow you to adjust the transparency of images. This is particularly useful for creating overlays, watermarks, and other design elements that require a transparent background.
Conclusion
Understanding the different image formats and their uses is essential for anyone working in graphic design, photography, or digital media. By choosing the right format for your needs, optimizing your images for different platforms, and using the right tools, you can ensure high-quality results in your projects. Whether you’re converting images to PNG or exploring other formats, this guide provides the insights you need to make informed decisions.